This is an unofficial archive of PsychonautWiki as of 2025-08-08T03:33:20Z. Content on this page may be outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate. Please refer to the original page for the most up-to-date information.
Pupil constriction: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>Oskykins m Text replacement - "===See also== *Responsible use=" to "===See also=== *Responsible use" |
>David Hedlund ===External links=== * [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miosis Miosis (Wikipedia)] |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
*[[Deliriants#Subjective_effects|Deliriants - Subjective effects]] | *[[Deliriants#Subjective_effects|Deliriants - Subjective effects]] | ||
*[[Pupil dilation|Pupil dilation]] | *[[Pupil dilation|Pupil dilation]] | ||
===External links=== | |||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Miosis Miosis (Wikipedia)] | |||
[[category:Physical]][[category:Novel]][[category:effect]] | [[category:Physical]][[category:Novel]][[category:effect]] | ||
Revision as of 08:33, 22 December 2017
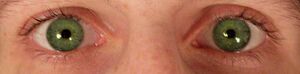
Pupil constriction (also called pinpoint pupils or miosis) is the reduction of the size of a person's pupils under normal lighting conditions. Pupil constriction decreases a person's ability to see in low light conditions. This effect generally occurs on opioids.
Psychoactive substances
Compounds within our psychoactive substance index which may cause this effect include:
- Acetylfentanyl
- Amanita muscaria
- Buprenorphine
- Clonidine
- Codeine
- Desomorphine
- Dextropropoxyphene
- Dihydrocodeine
- Diphenhydramine
- Ethylmorphine
- Fentanyl
- Gaboxadol
- Heroin
- Hydrocodone
- Hydromorphone
- Kratom
- Methadone
- Morphine
- Nicotine
- O-Desmethyltramadol
- Oxycodone
- Oxymorphone
- Pethidine
- Tapentadol
- Tizanidine
- Tramadol
- U-47700
See also
- Responsible use
- Subjective effects index
- Psychedelics - Subjective effects
- Dissociatives - Subjective effects
- Deliriants - Subjective effects
- Pupil dilation