This is an unofficial archive of PsychonautWiki as of 2025-08-08T03:33:20Z. Content on this page may be outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate. Please refer to the original page for the most up-to-date information.
Pupil constriction: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>Tracer Experience reports |
>Tracer Experience reports |
(No difference)
| |
Latest revision as of 13:19, 6 February 2020
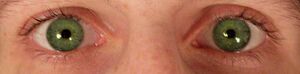
Pupil constriction (also called pinpoint pupils or miosis) can be described as the reduction of the size of a person's pupils under normal lighting conditions. This typically decreases a person's ability to see in low light conditions.
Pupil constriction is most commonly induced under the influence of moderate dosages of opioid compounds, such as heroin, kratom, tramadol, and fentanyl.
Psychoactive substances
Compounds within our psychoactive substance index which may cause this effect include:
- Acetylfentanyl
- Amanita muscaria
- Buprenorphine
- Clonidine
- Codeine
- Desomorphine
- Dextropropoxyphene
- Dihydrocodeine
- Diphenhydramine
- Ethylmorphine
- Fentanyl
- Gaboxadol
- Heroin
- Hydrocodone
- Hydromorphone
- Kratom
- Methadone
- Morphine
- Nicotine
- O-Desmethyltramadol
- Oxycodone
- Oxymorphone
- Pethidine
- Tapentadol
- Tizanidine
- Tramadol
- U-47700
Experience reports
Annectdotal reports which describe this effect with our experience index include:
See also
- Responsible use
- Subjective effects index
- Psychedelics - Subjective effects
- Dissociatives - Subjective effects
- Deliriants - Subjective effects
- Pupil dilation