Melatonin
Melatonin, also known as N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, is a naturally occurring compound found in animals, plants, and microbes. Melatonin, produced in the pineal gland which is outside of the blood–brain barrier, acts as an endocrine hormone since it is released into the blood. Many biological effects of melatonin are produced through activation of melatonin receptors, while others are due to its role as a pervasive and powerful antioxidant, with a particular role in the protection of nuclear and mitochondrial DNA.
Chemistry
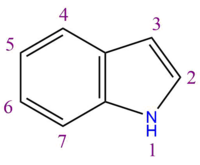
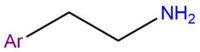
Melatonin is comprised of a monoamine chain attached to an indole ring at the third carbon. A monoamine chain is made up of an amine group attached to an ethane chain. This monoamine chain can be found in many neurotransmitters, including histamine, dopamine, adrenaline and noradrenaline. It's also found in many drugs, examples being tryptamines and phenethylamines.
Uses
Melatonin has many applications in the human body, including:
- Circadian rhythm and sleep cycles (biological clock).
- Antioxidant and free radical scavenger.
- Immune system enhancer.
- Dream activity enhancer.