User talk:Oskykins/Archive 1
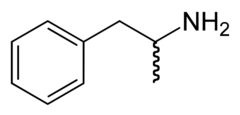
Amphetamine is a strong central nervous system stimulant that increases activity in the brain and induces temporary improvements including enhanced alertness, wakefulness, and locomotion. It is the parent compound of the substituted amphetamines class which also includes MDMA, methamphetamine. DOM, and DOC. The chemical structure of a substituted amphetamine is the same as the organic molecule amphetamine, except some substitutions are made at the phenyl and amine sites.
Amphetamine is widely used throughout the world as a prescription medicine for the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and the sleeping disorder narcolepsy.[1][2] It is also used without prescription as an illicit substance of recreational use or abuse.
Although the term amphetamine traditionally refers to an equal combination of the left-handed and right-handed enatiomers levoamphetamine (l-amphetamine) and dextroamphetamine (d-amphetamine), it is frequently used for any mixture of the two or only one of them. The prescription drug Adderall contains and The drug is usually taken orally, but can also be insufflated, injected, or administered rectally.
Chemistry
Pharmacology
"Amphetamine's action of causing dopamine to be released into the brain's synapses from the axon terminals is fairly well understood, but less well known is how each isomer of amphetamine accomplishes this task. Dextroamphetamine, the major component of Adderall, is thought to be most efficient at releasing dopamine along the brain's D1 and D4 pathways, which help focus cognitive attention. Levoamphetamine, the minor component of Adderall, is thought to be better at releasing norepinephrine and dopamine along the D2 reward pathways, causing rushes of euphoria and sexual arousal, as well as enhanced reflexes and motor coordination."
Subjective effects
Physical Effects
- Stimulation
- Dehydration
- Appetite suppression
- Nausea
- Frequent urination
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Vasconstriction
- Temporary Erectile Dysfunction
Cognitive Effects
- Acceleration of thought
- Increased Focus
- Enhancement of memory
- Increased motivation
- Euphoria
- Anxiety
- Depression
Toxicity and Harm Potential
Lethal Dosage
Tolerance and Addiction Potential
Legal Issues
See Also
References
- ↑ The pharmacology and clinical outcomes of amphetamines to treat ADHD: does composition matter? | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22329564
- ↑ Narcolepsy: current treatment options and future approaches |http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2526380/