Substituted amphetamines: Difference between revisions
>MDMQualone mNo edit summary |
>BronzeManul Removed 'phenethylamines' from the list of substance classes that are not included in the table. (All amphetamines are phenethylamines). Changed links to non-existent substance pages into plain text. Reworded intro paragraph. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:samphetamine.png|thumb|right|301px|| | [[File:samphetamine.png|thumb|right|301px||Substitutive structure of an ''amphetamine'' molecule.]] | ||
'''Substituted amphetamines''' are a | '''Substituted amphetamines''' (also known as '''amphetamines''') are a class of compounds with molecular structures based upon that the molecular structure of [[amphetamine]]. The class includes many [[Psychoactive substance index|psychoactive substances]], which typically produce [[stimulant]] effects, [[entactogen|entactogenic]] effects, and/or [[psychedelic]] effects. | ||
==Chemistry== | ==Chemistry== | ||
[[File:Phenethylamine.png|thumb|right|245px| | [[File:Phenethylamine.png|thumb|right|245px|Substitutive structure of a ''phenethylamine'' molecule.]] | ||
Substituted amphetamines are a class of | Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds that have structures based on that of [[amphetamine]] with different substitutions at various positions. An amphetamine molecule has the structure of a [[phenethylamine]] molecule with an additional methyl group located on the alpha carbon. Thus, in addition to being the unsubstituted member of the substituted amphetamine class, amphetamine is also considered a [[Phenethylamine|substituted phenethylamine]]. | ||
==Pharmacology== | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Psychoactive substances of the substituted amphetamine class typically produce effects through [[dopamine|dopaminergic]], [[serotonin|serotonergic]], and [[norepinephrine|adrenergic]] pathways. Psychedelic effects can be attributed to action on the [[Serotonin#The 5-HT system|5-HT<sub>2A</sub> receptor]].{{citation needed}} Stimulant and entactogenic effects are due to their action as [[Releasing Agent|releasing agents]] of [[dopamine]], [[serotonin]], [[epinephrine]] and [[norepinephrine]] or as [[Agonist#Agonists|agonists]] on the receptors of the previous neurotransmitters.{{citation needed}} The agonism of this set of receptors leads to an increased rate firing of the post-synaptic neuron, triggering both [[Thought acceleration|cognitive]] and [[Stimulation|physical stimulation]] within the user.{{citation needed}} | |||
== List of substituted amphetamines == | == List of substituted amphetamines == | ||
''Note: This list does not include [[ | ''Note: This list does not include [[Phenidate|phenidates]], [[Substituted cathinone|cathinones]], [[Substituted MDxx|MDxxs]], [[DOx|DOxs]], [[Benzofuran|Benzofurans]], or [[Substituted aminoindane|aminoindanes]].'' | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
| [[3-FEA]] || H || F || H || H || H || H || H || H || CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> || [[File:3-FEA.png|170px]] | | [[3-FEA]] || H || F || H || H || H || H || H || H || CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> || [[File:3-FEA.png|170px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Fenfluramine || H || CF<sub>3</sub> || H || H || H || H || H || H || CH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>3</sub> || [[File:Fenfluramine.png|170px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Norfenfluramine || H || CF<sub>3</sub> || H || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:Norfenfluramine.png|170px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[4-FA]] || H || H || F || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:4fa.png|170px]] | | [[4-FA]] || H || H || F || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:4fa.png|170px]] | ||
| Line 81: | Line 81: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4-CA || H || H || Cl || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:4-CA.png|170px]] | | 4-CA || H || H || Cl || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:4-CA.png|170px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4-BA || H || H || Br || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:4-BA.png|170px]] | | 4-BA || H || H || Br || H || H || H || H || H || H || [[File:4-BA.png|170px]] | ||
| Line 120: | Line 118: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
*[[Responsible use]] | *[[Responsible use]] | ||
*[[ | *[[Phenethylamine]] | ||
*[[Stimulants]] | *[[Stimulants]] | ||
*[[Entactogen]] | |||
*[[Psychedelic]] | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{references}} | {{references}} | ||
Revision as of 23:55, 12 April 2017
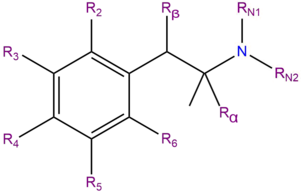
Substituted amphetamines (also known as amphetamines) are a class of compounds with molecular structures based upon that the molecular structure of amphetamine. The class includes many psychoactive substances, which typically produce stimulant effects, entactogenic effects, and/or psychedelic effects.
Chemistry
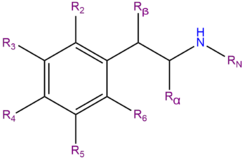
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds that have structures based on that of amphetamine with different substitutions at various positions. An amphetamine molecule has the structure of a phenethylamine molecule with an additional methyl group located on the alpha carbon. Thus, in addition to being the unsubstituted member of the substituted amphetamine class, amphetamine is also considered a substituted phenethylamine.
Pharmacology
Psychoactive substances of the substituted amphetamine class typically produce effects through dopaminergic, serotonergic, and adrenergic pathways. Psychedelic effects can be attributed to action on the 5-HT2A receptor.[citation needed] Stimulant and entactogenic effects are due to their action as releasing agents of dopamine, serotonin, epinephrine and norepinephrine or as agonists on the receptors of the previous neurotransmitters.[citation needed] The agonism of this set of receptors leads to an increased rate firing of the post-synaptic neuron, triggering both cognitive and physical stimulation within the user.[citation needed]
List of substituted amphetamines
Note: This list does not include phenidates, cathinones, MDxxs, DOxs, Benzofurans, or aminoindanes.
| Compound | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | Rα | Rβ | RN1 | RN2 | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 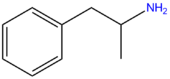
|
| Methamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 
|
| Ethylamphetamine (Etilamfetamine) | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 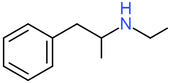
|
| Propylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH2CH3 | 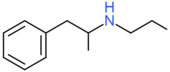
|
| Isopropylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | 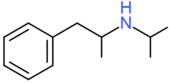
|
| Bromo-DragonFLY | OCH=CH- | - | Br | OCH=CH- | - | H | H | H | H | 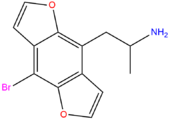
|
| Lisdexamfetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | COCH(NH2)(CH2)4NH2 | 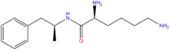
|
| Clobenzorex | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2C6H4Cl | 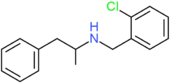
|
| Dimethylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | CH3 | 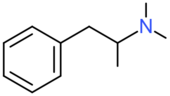
|
| Selegiline | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | CH2CCH | 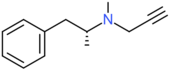
|
| Benzphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | CH2C6H5 | 
|
| Ortetamine | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 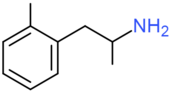
|
| 3-Methylamphetamine | H | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 
|
| 4-Methylamphetamine | H | H | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 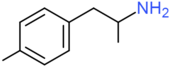
|
| 4-MMA | H | H | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 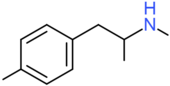
|
| Xylopropamine | H | CH3 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 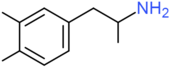
|
| β-methylamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | H | H | 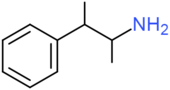
|
| β-phenylmethamphetamine | H | H | H | H | H | H | C6H5 | H | CH3 | 
|
| 2-FA | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 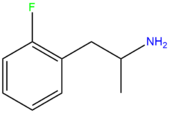
|
| 2-FMA | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 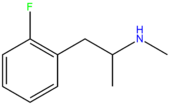
|
| 3-FA | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 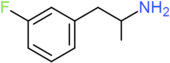
|
| 3-FMA | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 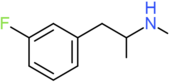
|
| 3-FEA | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | 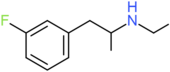
|
| Fenfluramine | H | CF3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | 
|
| Norfenfluramine | H | CF3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 
|
| 4-FA | H | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | H | 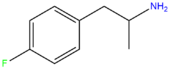
|
| 4-FMA | H | H | F | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 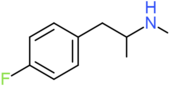
|
| 4-CA | H | H | Cl | H | H | H | H | H | H | 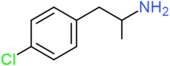
|
| 4-BA | H | H | Br | H | H | H | H | H | H | 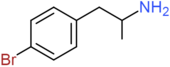
|
| 4-IA | H | H | I | H | H | H | H | H | H | 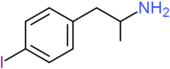
|
| DCA | H | Cl | Cl | H | H | H | H | H | H | 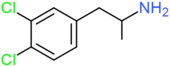
|
| 4-HA | H | H | OH | H | H | H | H | H | H | 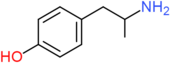
|
| 4-HMA | H | H | OH | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 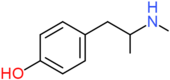
|
| 3,4-DHA | H | OH | OH | H | H | H | H | H | H | 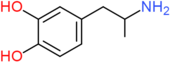
|
| OMA | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 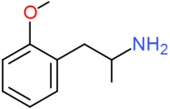
|
| 3-MA | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | H | 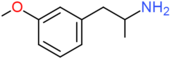
|
| MMMA | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 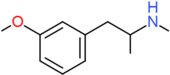
|
| MMA | H | OCH3 | CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 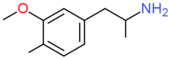
|
| PMA | H | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 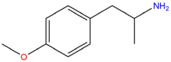
|
| PMMA | H | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | CH3 | 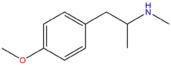
|
| PMEA | H | H | OCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | CH2CH3 | 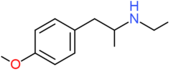
|
| 4-ETA | H | H | OCH2CH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 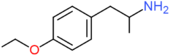
|
| 4-MTA | H | H | SCH3 | H | H | H | H | H | H | 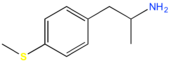
|
| Cathine | H | H | H | H | H | H | OH | H | H | 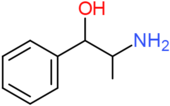
|
See also
References
 |
This article does not cite enough references. You can help by adding some. |