Datura: Difference between revisions
>Josikins |
>Josikins No edit summary |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
These are known as Scopolamine and Atropine, two molecules that are both in the tropane alkaloid class, with anticholinergic effects. The plants precise and natural distribution seems to be throughout most of the temperate and tropical regions of the globe, owing to its extensive cultivation and naturalization. There are a total of nine different species in the Datura genus, but the two most well-known species are Datura inoxia and Datura strammonium. Both of which have been used in a shamanic context for religious purposes on most continents since before recorded history began, with records of its use being found throughout the ancient americas, europe and india. | These are known as Scopolamine and Atropine, two molecules that are both in the tropane alkaloid class, with anticholinergic effects. The plants precise and natural distribution seems to be throughout most of the temperate and tropical regions of the globe, owing to its extensive cultivation and naturalization. There are a total of nine different species in the Datura genus, but the two most well-known species are Datura inoxia and Datura strammonium. Both of which have been used in a shamanic context for religious purposes on most continents since before recorded history began, with records of its use being found throughout the ancient americas, europe and india. | ||
As a general rule, [[ | As a general rule, [[PsychonautWiki]] neither recommends nor discourages the use of any psychoactive, however, in the case of tropane alkaloid-containing plants, we think it is important to note that an overwhelming majority of those who describe their use of Datura find their experiences extremely mentally and physically unpleasant and not infrequently physically dangerous. | ||
=Chemistry= | =Chemistry= | ||
Revision as of 01:23, 3 March 2014
| Datura | |
|---|---|
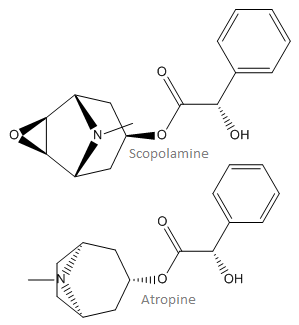 The skeletal formula of scopolomine and atropine. | |
| Dosage | |
| Differs wildly between plants. | |
| Duration | |
| Total Duration | 3 days |
| Onset | 60 - 120 minutes |
Datura is a genus of legal flowering plants that contains two psychoactive chemicals in roughly equal amounts.
These are known as Scopolamine and Atropine, two molecules that are both in the tropane alkaloid class, with anticholinergic effects. The plants precise and natural distribution seems to be throughout most of the temperate and tropical regions of the globe, owing to its extensive cultivation and naturalization. There are a total of nine different species in the Datura genus, but the two most well-known species are Datura inoxia and Datura strammonium. Both of which have been used in a shamanic context for religious purposes on most continents since before recorded history began, with records of its use being found throughout the ancient americas, europe and india.
As a general rule, PsychonautWiki neither recommends nor discourages the use of any psychoactive, however, in the case of tropane alkaloid-containing plants, we think it is important to note that an overwhelming majority of those who describe their use of Datura find their experiences extremely mentally and physically unpleasant and not infrequently physically dangerous.
Chemistry
Scopolamine and atropine, the active chemicals in datura, are both tropane alkaloids.
Pharmacology
Datura is an antimuscarinic agent.
Subjective effects
Physical effects
The physical effects of datura are usually described as extremely uncomfortable. They can be broken down into nine components all of which progressively intensify proportional to dosage. These are described below and generally include:
- Increased bodily weight - the first noticeable sensation being that of having an extremely heavy body, as if the gravity has been multiplied by a thousand. This makes it extremely difficult and uncomfortable to move.
- Spontaneous tactile sensations - users commonly report all encompassing, sharp and extremely painful jolts of electricity that spontaneously manifest themselves in a similar rhythm to hiccups.
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Restless leg syndrome
- Abnormal heart beat
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty urinating - this can be described as a feeling of concrete blocking your urethra and painfully conflicts with a frequent need to urinate.
Cognitive effects
The head space of datura is described by many as generally negative and dysphoric throughout the trip, generally consisting of extreme paranoia and feelings of impending doom. It is largely confusing and disorienting often leading to a complete inability to communicate or understand normal language. It contains unique cognitive effects found almost exclusively in the deliriant class.
The most prominent of these effects include:
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Thought deceleration
- Suppression of emotion
- Suppression of information processing
- Amnesia
- Suppression of language
- Time distortion
Datura does not enhance visual stimuli in the way that psychedelics do, instead they tend to degrade and decrease visual apptitude both increasing hallucination and degrading vision. These components are detailed below:
- Decreased visual acuity - this effect can result in blurry vision to the point of blindness, sometimes lasting for days after the trip itself.
- Suppression of pattern recognition
- Vibrating vision
As for visual distortions and alterations, effects experienced are detailed below:
- Visual drifting (Melting, Breathing, Morphing and Flowing) - in comparison to other hallucinogens this effect can be described as intricate in complexity, jittery, slow and rigid in motion,static in their permanence, realistic in believability, and interactive in plasticity
- Visual haze
- After images
The effects of Datura are extremely efficient at inducing delirious hallucinations which can be broken into the two categories described below:
Auditory effects
The auditory effects of Datura are common in their occurrence and exhibit a range of effects which commonly includes:
Natural plant sources

Datura is a genus of nine species of flowering plants, also known as angel's trumpets and daturas. Due to its extensive cultivation and naturalization throughout the temperate and tropical regions, it is found in most areas of the world. There are nine identified species:
- D. ceratocaula
- D. discolor
- D. ferox
- D. inoxia
- D. leichhardtii
- D. metel
- D. quercifolia
- D. stramonium
- D. wrightii
Toxicity and Harm Potential
Lethal Dosage
The LD50 for scopolamine in humans is 2µg/kg and for atropine is 33µg/kg.
It is extremely important to note however that the potency of plants varies wildly and there is no way for the common man to accurately measure the dosage. At high enough doses Datura becomes an incredibly toxic poison that can easily result in death, making Datura the most dangerous hallucinogen out there with accidental overdoses resulting in hospitalization not unheard of.
The safest way to ensure this does not happen is to grind the dried plant matter into an extremely fine and even powder so that the active chemicals within them are distributed evenly across itself. From here you can slowly work your way up in extremely small increments until the correct dosage for that particular plant is found.
If you want to try datura despite all of its risks, you can grow it yourself using seeds purchased online or find a wild plant in your local area.
Tolerance and Addiction Potential
Tolerance forms quickly with datura use. There is no real addictive potential.
Legal Issues
Datura grows naturally, is legal to grow, sell and consume, in most parts of the world.
- Australia: Datura is a Schedule I poison.
- Brazil: Possession and sale is illegal.