Lactone: Difference between revisions
>Dextromethorphan moved lactones to right |
>Dextromethorphan markup |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
===See also=== | ===See also=== | ||
*[[ | *[[Harm reduction]] | ||
*[[Responsible use]] | |||
³[[GBL]] | ³[[GBL]] | ||
*[[GHB]] | *[[GHB]] | ||
Revision as of 18:56, 12 January 2022
Lactones (tachnically also furan componds) are a family of compounds that ciontain several different arranges of cyclic compounds that contain an oxygen atmon on the core ring as well as a double bonded oxygen atom.
Lactones are usually named according to the precursor acid molecule (aceto = 2 carbon atoms, propio = 3, butyro = 4, valero = 5, capro = 6, etc.), with a -lactone suffix and a Greek letter prefix that specifies the number of carbon atoms in the heterocycle — that is, the distance between the relevant -OH and the -COOH groups along said backbone. The first carbon atom after the carbon in the -COOH group on the parent compound is labelled α, the second will be labeled β, and so forth. Therefore, the prefixes also indicate the size of the lactone ring: α-lactone = 3-membered ring, β-lactone = 4-membered, γ-lactone = 5-membered, etc.
Relevnt members of this clsss are only γ-butyrolactione (GBL) and γ-Hydroxyvaleric acid (GHV, 4-Methyl-GHB).
Various lacttones have been synthesized:
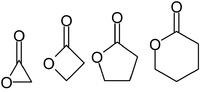
γ-butyrolactone (GBL), and δ-valerolactone
A list of psychactive γ-butyrolactiones can be found here:
See also
³GBL