Quetiapine: Difference between revisions
>Josikins |
>Josikins |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Subjective effects== | ==Subjective effects== | ||
===Physical effects=== | ===Physical effects=== | ||
*'''[[Physical effects: Sedation|Sedation]]''' | |||
*'''[[Physical effects: Dizziness|Dizziness]]''' | |||
*'''[[Physical effects: Dehydration|Dehydration]]''' | |||
===Cognitive effects=== | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Thought deceleration|Thought deceleration]]''' | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Suppression of emotion|Suppression of emotion]]''' | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Suppression of information processing|Suppression of information processing]]''' | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Suppression of language|Suppression of language]]''' | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Amnesia|Amnesia]]''' | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Ego suppression, loss and death|Ego suppression loss and death]]''' | |||
*'''[[Cognitive effects: Suppression of anxiety|Suppression of anxiety]]''' | |||
===Cognitive effects=== | ===Cognitive effects=== | ||
Revision as of 15:37, 30 April 2014
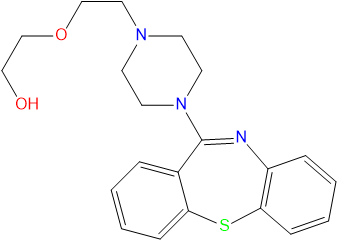
Quetiapine (/kwɨˈtaɪ.əpiːn/ kwi-ty-ə-peen) (branded as Seroquel, Xeroquel, Ketipinor) is a short-acting atypical antipsychotic approved for the treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and along with an antidepressant to treat major depressive disorder.
Annual sales are approximately $5.7 billion worldwide, with $2.9 billion in the United States.[1] The U.S. patent,[2] which was set to expire in 2011, received a pediatric exclusivity extension which pushed its expiration to March 26, 2012.[3][4] The patent has already expired in Canada. Quetiapine was developed by AstraZeneca from 1992-1996 as an improvement from first generation antipsychotics. It was first approved by the FDA in 1997. There are now several generic versions of quetiapine, such as Quepin, Syquel and Ketipinor.[5]
Chemistry
Pharmocology
This means Quetiapine is a dopamine, serotonin, and adrenergic antagonist, and a potent antihistamine with clinically negligible anticholinergic properties.[6][7][8][9] Quetiapine binds strongly to serotonin receptors; the drug acts as partial agonist at 5-HT1A receptors.[10] In terms of its antipsychotic effects, the precise mechanism of action is unknown, but according to the dopamine theory of schizophrenia, antipsychotic effects might be related to the drug’s ability to reduce dopaminergic neurotransmission in the mesolimbic pathway.
Subjective effects
Physical effects
Cognitive effects
- Thought deceleration
- Suppression of emotion
- Suppression of information processing
- Suppression of language
- Amnesia
- Ego suppression loss and death
- Suppression of anxiety
Cognitive effects
Toxicity and harm potential
Tolerance and addiction potential
Interactions
Legal issues
References
- ↑ http://drugpatentwatch.com/ultimate/preview/tradename/index.php?query=SEROQUEL
- ↑ http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-bool.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&co1=AND&d=PTXT&s1=4,879,288.PN.&OS=PN/4,879,288&RS=PN/4,879,288
- ↑ http://patft.uspto.gov/netacgi/nph-Parser?Sect1=PTO2&Sect2=HITOFF&p=1&u=%2Fnetahtml%2FPTO%2Fsearch-bool.html&r=1&f=G&l=50&co1=AND&d=PTXT&s1=4,879,288.PN.&OS=PN/4,879,288&RS=PN/4,879,288
- ↑ Blockbuster Drugs That Will Go Generic Soon | http://money.usnews.com/money/blogs/the-best-life/2011/04/29/blockbuster-drugs-that-will-go-generic-soon
- ↑ http://www.theodora.com/drugs/quepin_tablets_specifar.html
- ↑ http://www1.astrazeneca-us.com/pi/Seroquel.pdf
- ↑ Binding of antipsychotic drugs to human brain receptors: Focus on newer generation compounds | http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024320500009115
- ↑ Neuropsychopharmocology, a fifth generation of progress | http://books.google.co.uk/books?id=BKwkonZwZD0C&pg=PA778&hl=en#v=onepage&q&f=false
- ↑ http://www.drugs.com/pro/seroquel.html
- ↑ Mechanism of Action of Quetiapine | http://psychopharmacologyinstitute.com/antipsychotics/quetiapine/mechanism-of-action/