This is an unofficial archive of PsychonautWiki as of 2025-08-11T15:14:44Z. Content on this page may be outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate. Please refer to the original page for the most up-to-date information.
Beta-Carboline: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>PJosepherum mNo edit summary |
>PJosepherum mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:BetaCarboline.png|thumb|right| | [[File:BetaCarboline.png|thumb|right|257px|General formula of beta-carboline alkaloid molecule.]] | ||
'''Beta-carboline alkaloids''' (β-carbolines) are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects. They are often combined with [[ayahuasca]] brews, to prevent the breakdown of [[DMT]] in the digestive system by inhibiting the enzyme [[MAOI|monoamine oxidase]]. | '''Beta-carboline alkaloids''' (β-carbolines) are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects. They are often combined with [[ayahuasca]] brews, to prevent the breakdown of [[DMT]] in the digestive system by inhibiting the enzyme [[MAOI|monoamine oxidase]]. | ||
Revision as of 21:13, 29 April 2014
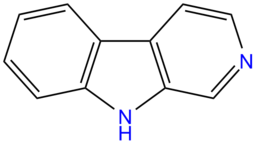
Beta-carboline alkaloids (β-carbolines) are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects. They are often combined with ayahuasca brews, to prevent the breakdown of DMT in the digestive system by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase.
Chemistry
Beta-carboline alkaloids are based upon the molecule beta-Carboline. beta-Carboline itself is made up of an indole ring attached to a pyridine ring.
Examples
Beta-carbolines are seen throughout organic chemistry and include psychoactive drugs.