This is an unofficial archive of PsychonautWiki as of 2025-08-11T15:14:44Z. Content on this page may be outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate. Please refer to the original page for the most up-to-date information.
Substituted phenidates: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>Unity added to category. |
>Unity Expand to include information on pharmacological mechanism. Grammatics. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:sphenidate.png|thumb|right|301px||Generic structure of a phenidate molecule.]] | [[File:sphenidate.png|thumb|right|301px||Generic structure of a phenidate molecule.]] | ||
'''Substituted phenidates''' | '''Substituted phenidates''' (also known as '''phenidates''') are a class of chemicals that include compounds that typically produce traditional [[stimulant]] effects. Pharmacologically, they tend to act as [[reuptake inhibitors]] of the [[monoamine]] [[neurotransmitters]] [[dopamine]] and [[norepinephrine]], and occasionally [[serotonin]].{{citation needed}} | ||
==Chemistry== | ==Chemistry== | ||
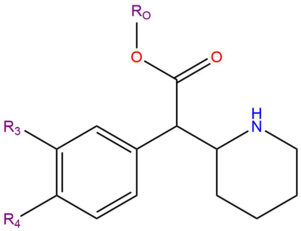
Substituted phenidates are a chemical class based upon the molecule [[ | Substituted phenidates are a chemical class based upon the molecule [[methylphenidate]]. The molecular structure of methylphenidate is comprised of a [[Substituted Phenethylamines|phenethylamine]] core with a carbon chain substitution at the R<sub>α</sub> position that links to the R<sub>N</sub> position, forming a piperidine ring. It also includes a substitution at the R<sub>β</sub> position of methyl acetate. | ||
== List of substituted phenidates == | == List of substituted phenidates == | ||
Revision as of 22:50, 6 August 2017
Substituted phenidates (also known as phenidates) are a class of chemicals that include compounds that typically produce traditional stimulant effects. Pharmacologically, they tend to act as reuptake inhibitors of the monoamine neurotransmitters dopamine and norepinephrine, and occasionally serotonin.[citation needed]
Chemistry
Substituted phenidates are a chemical class based upon the molecule methylphenidate. The molecular structure of methylphenidate is comprised of a phenethylamine core with a carbon chain substitution at the Rα position that links to the RN position, forming a piperidine ring. It also includes a substitution at the Rβ position of methyl acetate.
List of substituted phenidates
| Compound | R3 | R4 | RO | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methylphenidate | H | H | CH3 | 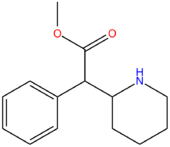
|
| Ethylphenidate | H | H | CH2CH3 | 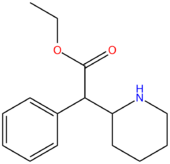
|
| Isopropylphenidate | H | H | CH(CH3)2 | 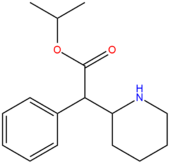
|
| Propylphenidate | H | H | CH2CH2CH3 | 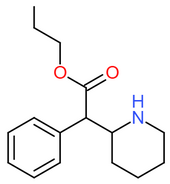
|
| 4-Methyl Methylphenidate | H | CH3 | CH3 | 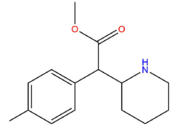
|
| 3,4-CTMP | Cl | Cl | CH3 | 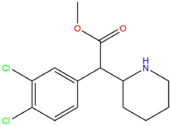
|
| 4F-MPH | H | F | CH3 | 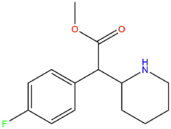
|
| 4F-EPH | H | F | CH2CH3 | 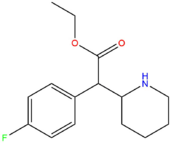
|
| Methylnaphthidate (HDMP-28) | CH=CH- | CH=CH- | CH3 | 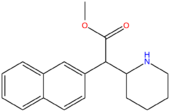
|
| Ethylnaphthidate | CH=CH- | CH=CH- | CH2CH3 | 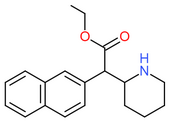
|