Transpersonal effects: Difference between revisions
>Josikins No edit summary |
>Josikins No edit summary |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*[[Novel cognitive states]] | *[[Novel cognitive states]] | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Revision as of 03:15, 10 June 2016
Spiritual states can be defined as any novel cognitive effect which feels as if it relates to or contains information regarding one's place in the universe, the inner workings of reality, the context of their existence or their purpose in life. These can occur regardless of one's religious beliefs and often have a distinct and lasting impact on the user's perspective of the world around them. During the experience of a spiritual state, the information conveyed is felt to be a real and objective truth although the user may later disagree with the revelations once the effects of the drug have worn off.
This page lists and describes the various spiritual states which can occur under the influence of certain psychoactive compounds such as psychedelics.
Feelings of eternalism
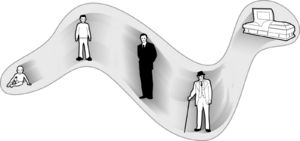
Perception of eternalism can be described as the experience of a major alteration of one's perspective of the fundamental mechanics behind the linear continuity of time moving from the past to the present to the future. During this state of mind, it feels as if all points across the timeline of existence are equally "real" and are occurring simultaneously alongside each other. Every point in time is felt to exist regardless of the person's current position within the overall timeline, much as all points in physical space persist regardless of the observer's location. However, it is important to understand that these conclusions and feelings should not be accepted at face value as inherently true.
While all moments are felt to be equally real, the directional flow of time is felt to be maintained, with the present always being the moment which is currently experienced. All moments in time are still felt to be linked together by causality, the past necessitating the present, which necessitates the future, and so forth.
A common conclusion that is reached during the experience of this state is that although one's life inevitably will end, it will apparently persist forever within its own timeframe and is therefore perpetual despite not being infinite in its length. Birth and death are therefore merely the start and end points of the range of time that a person exists in eternally, if not experiences eternally.
This sudden change in perspective starkly contrasts with the standard perception of time in which only the present is felt to exist, while the past no longer is and the future is yet to be.
Perception of eternalism is often accompanied by other coinciding transpersonal effects such as unity and interconnectedness and feelings of interdependent opposites. It is most commonly induced under the influence of heavy dosages of psychedelic compounds, such as LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline.
Feelings of interdependent opposites

Perception of interdependent opposites can be described as the experience of a powerful subjective feeling that reality is based upon a binary system in which the existence of fundamentally important concepts or situations logically arise from and depend upon the co-existence of their opposite. This perception is not just understood at a cognitive level, but manifests as intuitive sensations which are felt rather than thought by the person.
This experience is usually interpreted as providing a deep insight into the fundamental nature of reality. For example, concepts such as existence and non-existence, life and death, up and down, self and other, light and dark, good and bad, big and small, pleasure and suffering, yes and no, internal and external, hot and cold, young and old, etc are felt to exist as harmonious forces which necessarily contrast their opposite force in a state of equilibrium.
Perception of interdependent opposites is often accompanied by other coinciding transpersonal effects such as ego dissolution, unity and interconnectedness, and perception of eternalism. It is most commonly induced under the influence of heavy dosages of psychedelic compounds, such as LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline.
Feelings of predeterminism
Perception of predeterminism can be described as the sensation that all physical and mental processes are the result of prior causes, that every event and choice is an inevitable outcome that could not have happened differently, and that all of reality is a complex causal chain that can be traced back to the beginning of time. This is accompanied by the absence of the feeling that a person's decision-making processes and general cognitive faculties inherently possess "free will”. This sudden change in perspective causes the person to feel as if their personal choices, physical actions, and individual personality traits have always been completely predetermined by prior causes and are, therefore, outside of their conscious control.
During this state, a person begins to feel as if their decisions arise from a complex set of internally stored, pre-programmed, and completely autonomous, instant electrochemical responses to perceived sensory input. These sensations are often interpreted as somehow disproving the concept of free will, as the experience of this effect feels as if it is fundamentally incompatible with the notion of being self-determined. This state can also lead a person to the conclusion that their very identity and selfhood are the cumulative results of their biology and past experiences.
Once the effect begins to wear off, a person will often return to their everyday feelings of freedom and independence. Despite this, however, they will often retain realizations regarding what is often interpreted as a profound insight into the apparent illusory nature of free will.
Perception of predeterminism is often accompanied by other coinciding effects such as ego dissolution and physical autonomy. It is most commonly induced under the influence of heavy dosages of psychedelic compounds, such as LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline.
Feelings of self-design
Perception of self-design can be described as the experience of feeling that one is personally responsible for the creation, design, manifestation of a concept, process, or event which is normally seen as the result of unrelated external causes. It can be broken down into two separate sub-components which include:
- Feeling as if one designed, planned out, and created certain, or even all aspects of one's life such as current or past events, loved ones, and key events.
- Feeling as if one designed, planned out and created certain, or even all, aspects of the external world such as current or historical events, nature, life, the universe as a whole, and the physical laws which it abides by.
This effect typically occurs suddenly and spontaneously. However, it is most commonly felt during emotionally significant situations which are so enjoyable and fulfilling that they are exactly how the person would have designed it had they have somehow been given the conscious choice to do so in advance. This is especially true of situations that seem improbable or are completely unexpected.
Perception of self-design is often accompanied by other coinciding effects such as ego dissolution, delusions of grandiosity and high level unity and interconnectedness. It is most commonly induced under the influence of heavy dosages of psychedelic compounds, such as LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline.
Spirituality enhancement
Spirituality intensification is defined as the experience of a shift in a person’s personal beliefs regarding their existence and place within the universe, their relationship to others, and what they value as meaningful in life. It results in a person rethinking the significance they place on certain key concepts, holding some in higher regard than they did previously, and dismissing others as less important.[1] These concepts and notions are not limited to but generally include:
- An increased sense of personal purpose.[2]
- An increased interest in the pursuit of developing personal religious and spiritual ideologies.[3][4]
- The formation of complex personal religious beliefs.
- An increased sense of compassion towards nature and other people.[3][4][5]
- An increased sense of unity and interconnectedness between oneself, nature, "god", and the universe as a whole.[1][3][5][6][7][8][9]
- A decreased sense of value placed upon money and material objects.[5]
- A decreased fear and greater acceptance of death and the finite nature of existence.[1][10][11]
Although difficult to fully specify due to the subjective aspect of spirituality intensification, these changes in to a person's belief system can often result in profound changes in a person's personality[5][7][12] which can sometimes be distinctively noticeable to the people around those who undergo it. This shift can occur suddenly but will usually increase gradually over time as a person repeatedly uses the psychoactive substance which is inducing it.
Spirituality intensification is unlikely to be an isolated effect component but rather the result of a combination of an appropriate setting[3] in conjunction with other coinciding effects such as analysis enhancement, autonomous voice communication, novelty enhancement, perception of interdependent opposites, perception of predeterminism, perception of self-design, personal bias suppression, and unity and interconnectedness. It is most commonly induced under the influence of moderate dosages of psychedelic compounds, such as LSD, psilocybin, and mescaline. However, it can also occur to a lesser extent under the influence of dissociatives, such as ketamine, PCP, and DXM.
Unity and interconnectedness
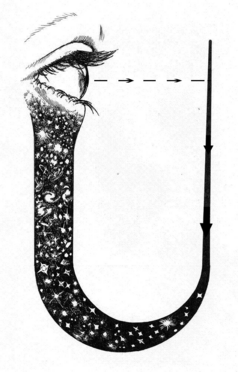
Unity and interconnectedness can be described as the experience of one's sense of self becoming temporarily changed to feel as if it is constituted by a wider array of concepts than that which it previously did. For example, while a person may usually feel that they are exclusively their “ego” or a combination of their “ego” and physical body, during this state their sense of identity can change to also include the external environment or an object they are interacting with. This results in intense and inextricable feelings of unity or interconnectedness between oneself and varying arrays of previously "external" systems.
It is worth noting that many people who undergo this experience consistently interpret it as the removal of a deeply embedded illusion, the destruction of which is often described as some sort of profound “awakening” or “enlightenment.” However, it is important to understand that these conclusions and feelings should not necessarily be accepted at face value as inherently true.
Unity and interconnectedness most commonly occurs under the influence of psychedelic and dissociative compounds such as LSD, DMT, ayahuasca, mescaline, and ketamine. However it can also occur during well-practiced meditation, deep states of contemplation, and intense focus.
There are a total of 5 distinct levels of identity which a person can experience during this state. These various altered states of unity have been arranged into a leveling system that orders its different states from least to the most number of concepts that one's identity is currently attributed to. These levels are described below:
1. Unity between specific "external" systems
At the lowest level, this effect can be described as a perceived sense of unity between two or more systems within the external environment which in everyday life are usually perceived as separate from each other. This is the least complex level of unity, as it is the only level of interconnectedness in which the subjective experience of unity does not involve a state of interconnectedness between the self and the external.
There are an endless number of ways in which this level can manifest, but common examples of the experience often include:
- A sense of unity between specific living things such as animals or plants and their surrounding ecosystems.
- A sense of unity between other human beings and the objects they are currently interacting with.
- A sense of unity between any number of currently perceivable inanimate objects.
- A sense of unity between humanity and nature.
- A sense of unity between literally any combination of perceivable external systems and concepts.
2. Unity between the self and specific "external" systems
At this level, unity can be described as feeling as if one's identity is attributed to (in addition to the body and/or brain) specific external systems or concepts within the immediate environment, particularly those that would usually be considered as intrinsically separate from one's own being.
The experience itself is often described as a loss of perceived boundaries between a person’s identity and the specific physical systems or concepts within the perceivable external environment which are currently the subject of a person's attention. This creates a sensation of becoming inextricably "connected to", "one with", "the same as", or "unified" with whatever the perceived external system happens to be.
There are an endless number of ways in which this level can manifest itself, but common examples of the experience often include:
- Becoming unified with and identifying with a specific object one is interacting with.
- Becoming unified with and identifying with another person or multiple people, particularly common if engaging in sexual or romantic activities.
- Becoming unified with and identifying with the entirety of one's own physical body.
- Becoming unified with and identifying with large crowds of people, particularly common at raves and music festivals.
- Becoming unified with and identifying with the external environment, but not the people within it.
3. Unity between the self and all perceivable "external" systems
At this level, unity can be described as feeling as if one's identity is attributed to the entirety of their immediately perceivable external environment due to a loss of perceived boundaries between the previously separate systems.
The effect creates a sensation in the person that they have become "one with their surroundings.” This is felt to be the result of a person’s sense of self becoming attributed to not just primarily the internal narrative of the ego, but in equal measure to the body itself and everything around it which it is physically perceiving through the senses. It creates the compelling perspective that one is the external environment experiencing itself through a specific point within it, namely the physical sensory perceptions of the body that one's consciousness is currently residing in.
It is at this point that a key component of the high-level unity experience becomes an extremely noticeable factor. Once a person's sense of self has become attributed to the entirety of their surroundings, this new perspective completely changes how it feels to physically interact with what was previously felt to be an external environment. For example, when one is not in this state and is interacting with a physical object, it typically feels as though one is a central agent acting on the separate world around them. However, while undergoing a state of unity with the currently perceivable environment, interacting with an external object consistently feels as if the whole unified system is autonomously acting on itself with no central, separate agent operating the process of interaction. Instead, the process suddenly feels as if it has become completely decentralized and holistic, as the environment begins to autonomously and harmoniously respond to itself in a predetermined manner to perform the interaction carried out by the individual.
4. Unity between the self and all known "external" systems
At the highest level, this effect can be described as feeling as if one's identity is simultaneously attributed to the entirety of the immediately perceivable external environment and all known concepts that exist outside of it. These known concepts typically include all of humanity, nature, and the universe as it presently stands in its complete entirety. This feeling is commonly interpreted by people as "becoming one with the universe".
When experienced, the effect creates the sudden perspective that one is not a separate agent approaching an external reality, but is instead the entire universe as a whole experiencing itself, exploring itself, and performing actions upon itself through the specific point in space and time which this particular body and conscious perception happens to currently reside within. People who undergo this experience consistently interpret it as the removal of a deeply embedded illusion, with the revelation often described as some sort of profound “awakening” or “enlightenment.”
Although they are not necessarily literal truths about reality, at this point, many commonly reported conclusions of a religious and metaphysical nature often begin to manifest themselves as profound realizations. These are described and listed below:
- The sudden and total acceptance of death as a fundamental complement of life. Death is no longer felt to be the destruction of oneself, but simply the end of this specific point of a greater whole, which has always existed and will continue to exist and live on through everything else in which it resides. Therefore, the death of a small part of the whole is seen as an inevitable, and not worthy of grief or any emotional attachment, but simply a fact of reality.
- The subjective perspective that one's preconceived notions of "god" or deities can be felt as identical to the nature of existence and the totality of its contents, including oneself. This typically entails the intuition that if the universe contains all possible power (omnipotence), all possible knowledge (omniscience), is self-creating, and self-sustaining then on either a semantic or literal level the universe and its contents could also be viewed as a god.
- The subjective perspective that one, by nature of being the universe, is personally responsible for the design, planning, and implementation of every single specific detail and plot element of one's personal life, the history of humanity, and the entirety of the universe. This naturally includes personal responsibility for all humanity's sufferings and flaws but also includes its acts of love and achievements.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Gasser, P., Kirchner, K., Passie, T. (January 2015). "LSD-assisted psychotherapy for anxiety associated with a life-threatening disease: A qualitative study of acute and sustained subjective effects". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 29 (1): 57–68. doi:10.1177/0269881114555249. ISSN 0269-8811.
- ↑ Peterman, A. H., Fitchett, G., Brady, M. J., Hernandez, L., Cella, D. (February 2002). "Measuring spiritual well-being in people with cancer: The functional assessment of chronic illness therapy—spiritual well-being scale (FACIT-Sp)". Annals of Behavioral Medicine. 24 (1): 49–58. doi:10.1207/S15324796ABM2401_06. ISSN 0883-6612.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Trichter, S., Klimo, J., Krippner, S. (June 2009). "Changes in Spirituality Among Ayahuasca Ceremony Novice Participants". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 41 (2): 121–134. doi:10.1080/02791072.2009.10399905. ISSN 0279-1072.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Griffiths, R. R., Johnson, M. W., Richards, W. A., Richards, B. D., McCann, U., Jesse, R. (December 2011). "Psilocybin occasioned mystical-type experiences: immediate and persisting dose-related effects". Psychopharmacology. 218 (4): 649–665. doi:10.1007/s00213-011-2358-5. ISSN 0033-3158.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Lerner, M., Lyvers, M. (June 2006). "Values and Beliefs of Psychedelic Drug Users: A Cross-Cultural Study". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 38 (2): 143–147. doi:10.1080/02791072.2006.10399838. ISSN 0279-1072.
- ↑ Griffiths, R. R., Richards, W. A., McCann, U., Jesse, R. (August 2006). "Psilocybin can occasion mystical-type experiences having substantial and sustained personal meaning and spiritual significance". Psychopharmacology. 187 (3): 268–283. doi:10.1007/s00213-006-0457-5. ISSN 0033-3158.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 MacLean, K. A., Johnson, M. W., Griffiths, R. R. (November 2011). "Mystical experiences occasioned by the hallucinogen psilocybin lead to increases in the personality domain of openness". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 25 (11): 1453–1461. doi:10.1177/0269881111420188. ISSN 0269-8811.
- ↑ Kometer, M., Pokorny, T., Seifritz, E., Volleinweider, F. X. (October 2015). "Psilocybin-induced spiritual experiences and insightfulness are associated with synchronization of neuronal oscillations". Psychopharmacology. 232 (19): 3663–3676. doi:10.1007/s00213-015-4026-7. ISSN 0033-3158.
- ↑ Lyvers, M., Meester, M. (1 November 2012). "Illicit Use of LSD or Psilocybin, but not MDMA or Nonpsychedelic Drugs, is Associated with Mystical Experiences in a Dose-Dependent Manner". Journal of Psychoactive Drugs. 44 (5): 410–417. doi:10.1080/02791072.2012.736842. ISSN 0279-1072.
- ↑ Ross, S., Bossis, A., Guss, J., Agin-Liebes, G., Malone, T., Cohen, B., Mennenga, S. E., Belser, A., Kalliontzi, K., Babb, J., Su, Z., Corby, P., Schmidt, B. L. (December 2016). "Rapid and sustained symptom reduction following psilocybin treatment for anxiety and depression in patients with life-threatening cancer: a randomized controlled trial". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 30 (12): 1165–1180. doi:10.1177/0269881116675512. ISSN 0269-8811.
- ↑ Grob, C. S., Danforth, A. L., Chopra, G. S., Hagerty, M., McKay, C. R., Halberstadt, A. L., Greer, G. R. (3 January 2011). "Pilot Study of Psilocybin Treatment for Anxiety in Patients With Advanced-Stage Cancer". Archives of General Psychiatry. 68 (1): 71. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.116. ISSN 0003-990X.
- ↑ Studerus, E., Kometer, M., Hasler, F., Vollenweider, F. X. (November 2011). "Acute, subacute and long-term subjective effects of psilocybin in healthy humans: a pooled analysis of experimental studies". Journal of Psychopharmacology. 25 (11): 1434–1452. doi:10.1177/0269881110382466. ISSN 0269-8811.