Substituted tropanes: Difference between revisions
>Josikins m Josifikins moved page Tropane Alkaloids to Tropane Alkaloid |
>David Hedlund {{#set:Featured=true}} |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:tropane.png|thumb| | [[File:tropane.png|thumb|200px|right|General tropane molecule]] | ||
''' | {{Stub}} | ||
'''Substituted tropanes''' (or simply '''tropanes''') are a group of [[psychoactive compounds]] that include a tropane ring in their structure. Prominent examples include certain [[stimulants]] like [[cocaine]] and its derivatives as well as [[deliriants]] like [[atropine]] and [[scopolamine]]. | |||
==Chemistry== | ==Chemistry== | ||
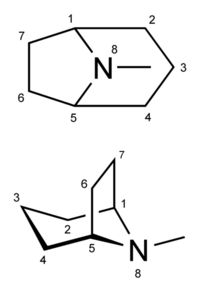
Tropanes are molecules which contain a substituted tropane ring in their structure. Tropane is a nitrogen-containing bicyclic organic molecule which consists of a [[piperidine]] and [[pyrrolidine]] ring fused at carbons R<sub>1</sub> and R<sub>5</sub> along with an additional methyl substitution at R<sub>N</sub>. It is mainly known for a group of [[alkaloids]] derived from it. Tropane alkaloids are commonly substituted at R<sub>3</sub> with an ether bridge (as seen in [[scopolamine]], [[atropine]], [[hyoscyamine]], and [[cocaine]]). Synthetic analogs of tropane alkaloids also exist, such as the phenyltropanes. They are not considered to be alkaloids per definition. | |||
==Pharmacology== | ==Pharmacology== | ||
Tropane alkaloids are mostly [[Acetylcholine#The | {{pharmacology}} | ||
Tropane alkaloids are mostly [[Acetylcholine#The cholinergic system|anti-cholinergics]] (antagonistic action on acetylcholine [[receptors]]) or [[stimulant]]s (prevention of [[dopamine]] reuptake). | |||
== | ==List of substituted tropanes== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|- | |||
! scope="col" | '''Compound''' | |||
! scope="col" style="width: 50px;" | '''R<sub>2</sub>''' | |||
! scope="col" style="width: 50px;" | '''R<sub>3</sub>''' | |||
! scope="col" style="width: 50px;" | '''R<sub>6</sub>''' | |||
! scope="col" style="width: 50px;" | '''R<sub>7</sub>''' | |||
! scope="col" | '''Structure''' | |||
|- | |||
| [[Atropine]] || H || OCOCH(CH<sub>2</sub>OH)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub> || H || H || [[File:Atropine.svg|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Hyoscyamine]] || H || OCOCH(CH<sub>2</sub>OH)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub> || H || H || [[File:Hyoscyamine.svg|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Scopolamine]] || H || OCOCH(CH<sub>2</sub>OH)C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub> || O- || - || [[File:Scopolamine.svg|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Cocaine]] || CO</sub>2</sub>CH</sub>3</sub> || OCOC<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub> || H || H || [[File:Cocaine.svg|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[Troparil]] || CO</sub>2</sub>CH</sub>3</sub> || C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>5</sub> || H || H || [[File:Troparil.svg|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
| [[RTI-111]] || CO</sub>2</sub>CH</sub>3</sub> || C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>3</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> || H || H || [[File:RTI-111.svg|170px]] | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
==External links== | |||
*[ | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tropane Tropane (Wikipedia)] | ||
*[[wikipedia:Tropane alkaloid|Tropane alkaloid (Wikipedia)]] | |||
*[[ | |||
==References== | |||
{{references}} | |||
[[Category:Chemical class]] | |||
[[Category:Tropane|*]] | |||
= | {{#set:Featured=true}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:09, 21 April 2024
 |
This article is a stub. As such, it may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding it. |
Substituted tropanes (or simply tropanes) are a group of psychoactive compounds that include a tropane ring in their structure. Prominent examples include certain stimulants like cocaine and its derivatives as well as deliriants like atropine and scopolamine.
Chemistry
Tropanes are molecules which contain a substituted tropane ring in their structure. Tropane is a nitrogen-containing bicyclic organic molecule which consists of a piperidine and pyrrolidine ring fused at carbons R1 and R5 along with an additional methyl substitution at RN. It is mainly known for a group of alkaloids derived from it. Tropane alkaloids are commonly substituted at R3 with an ether bridge (as seen in scopolamine, atropine, hyoscyamine, and cocaine). Synthetic analogs of tropane alkaloids also exist, such as the phenyltropanes. They are not considered to be alkaloids per definition.
Pharmacology
 |
This pharmacology section is incomplete. You can help by adding to it. |
Tropane alkaloids are mostly anti-cholinergics (antagonistic action on acetylcholine receptors) or stimulants (prevention of dopamine reuptake).
List of substituted tropanes
| Compound | R2 | R3 | R6 | R7 | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atropine | H | OCOCH(CH2OH)C6H5 | H | H | 
|
| Hyoscyamine | H | OCOCH(CH2OH)C6H5 | H | H | 
|
| Scopolamine | H | OCOCH(CH2OH)C6H5 | O- | - | 
|
| Cocaine | CO2CH3 | OCOC6H5 | H | H | 
|
| Troparil | CO2CH3 | C6H5 | H | H | 
|
| RTI-111 | CO2CH3 | C6H3Cl2 | H | H | 
|
External links
References
 |
This article does not cite enough references. You can help by adding some. |