This is an unofficial archive of PsychonautWiki as of 2025-08-08T03:33:20Z. Content on this page may be outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate. Please refer to the original page for the most up-to-date information.
Substituted morphinans: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>Oskykins m Text replace - "See Also" to "See also" |
>Josikins No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
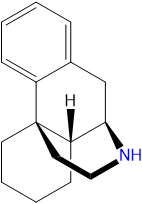
[[File:Morphinan2.png|thumb|142px|right|General formula of morphinan molecule.]]{{stub}} | |||
[[File:Morphinan2.png|thumb|142px|right|General formula of morphinan molecule.]] | |||
'''Morphinans''' are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects. | '''Morphinans''' are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 11: | ||
Morphinans are seen throughout organic chemistry, including many analgesic, antitussive and anaesthetic compounds. | Morphinans are seen throughout organic chemistry, including many analgesic, antitussive and anaesthetic compounds. | ||
====Dissociative Drugs==== | |||
*[[DXM]] | *[[DXM]] | ||
====Analgesic Drugs==== | |||
*Levomethorphan | *Levomethorphan | ||
*Phenomorphan | *Phenomorphan | ||
Revision as of 22:39, 18 April 2015
 |
This article is a stub. As such, it may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding it. |
Morphinans are a class of chemicals that include compounds with psychoactive effects.
Chemistry
Morphinans are made up of the morphinan molecule, with altering functional groups attached on the numbered carbons.
Pharmacology
The morphinans are a large chemical class and compounds within it have differing pharmacological effects. These include action upon the NMDA receptor, the μ-opioid receptor and the σ1 and σ2 sigma receptors.
Examples
Morphinans are seen throughout organic chemistry, including many analgesic, antitussive and anaesthetic compounds.
Dissociative Drugs
Analgesic Drugs
- Levomethorphan
- Phenomorphan
- Nalbuphine