This is an unofficial archive of PsychonautWiki as of 2025-08-08T03:33:20Z. Content on this page may be outdated, incomplete, or inaccurate. Please refer to the original page for the most up-to-date information.
K-Opioid receptor agonist: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
>Corticosteroid m addition |
>White Grammatics, category added |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{stub}} | {{stub}} | ||
[[File:Salvia.png|245px|thumbnail|Salvinorin A - The commonly used k-opioid receptor agonist.]] | [[File:Salvia.png|245px|thumbnail|Salvinorin A - The commonly used k-opioid receptor agonist.]] | ||
''' | '''κ-opioid receptor [[agonists]]''' are [[psychoactive drug]]s, which induce atypical [[hallucinogen]]ic effects. | ||
They bind to the | They bind to the kappa opioid receptors with varying affinities. | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
* [[Salvinorin A]] | * [[Salvinorin A]] | ||
* [[Salvinorin B]] | * [[Salvinorin B]] | ||
* [[Ibogaine]] | * [[Ibogaine]] | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Responsible use]] | * [[Responsible use]] | ||
* [[Dissociative]] | * [[Dissociative]] | ||
* [[Antagonist]] | * [[Antagonist]] | ||
[[Category:Neuroscience]] | |||
Revision as of 15:02, 14 August 2017
 |
This article is a stub. As such, it may contain incomplete or wrong information. You can help by expanding it. |
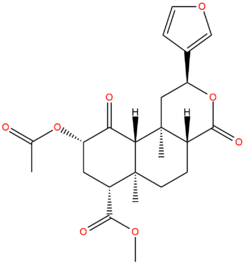
κ-opioid receptor agonists are psychoactive drugs, which induce atypical hallucinogenic effects. They bind to the kappa opioid receptors with varying affinities.